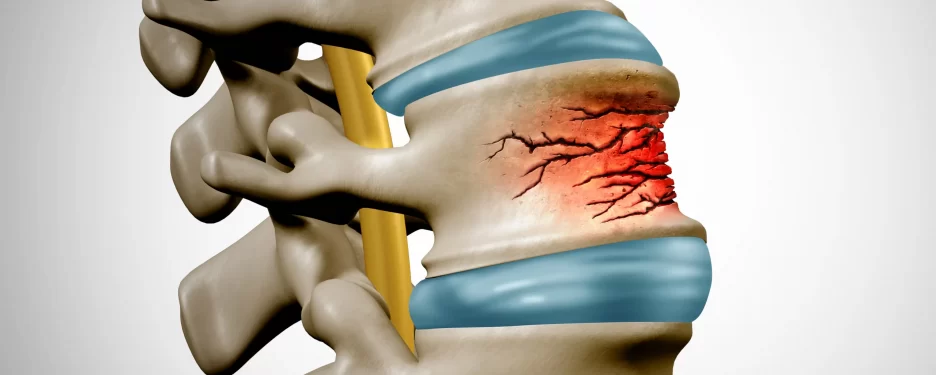
Sports is a physically demanding activity that requires a lot of effort, endurance and strength from athletes. However, sometimes, the stress placed on bones can lead to injuries, such as stress fractures. Stress fractures are tiny cracks in bones that develop due to repetitive stress and overuse. These injuries are common among athletes and can cause severe pain, discomfort and long-term damage if left untreated.
Causes of Stress Fractures in Sports People
Stress fractures are caused by repetitive stress and overuse of bones. Athletes who engage in high-impact sports are at a higher risk of developing stress fractures. Common causes of stress fractures include:
- Overtraining
- Increasing the intensity or duration of training too quickly
- Poor technique or form
- Worn-out shoes or equipment
- Nutritional deficiencies, such as low calcium or vitamin D levels
Symptoms of Stress Fractures
The symptoms of stress fractures include pain, swelling, tenderness and discomfort in the affected area. Athletes may also experience pain during physical activity, which may worsen over time. In some cases, stress fractures may cause visible swelling or a noticeable bump on the affected bone.
Treatment Options for Stress Fractures
Treatment for stress fractures depends on the severity of the injury. Common treatment options include:
- Rest: Athletes are advised to avoid physical activity and rest the affected bone to allow it to heal. This may take several weeks or months, depending on the severity of the injury.
- Ice: Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Compression: Wearing a compression bandage or brace can help reduce swelling and provide support to the affected area.
- Elevation: Elevating the affected area above the heart can help reduce swelling and promote healing.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relief medication, such as ibuprofen, can help reduce pain and discomfort.
Recovery Time for Stress Fractures
The recovery time for stress fractures varies depending on the severity of the injury and the location of the fracture. In general, athletes can expect a recovery time of 6 to 8 weeks for minor stress fractures. However, more severe stress fractures may take several months to heal completely. During this time, athletes are advised to avoid physical activity and follow their doctor's instructions for recovery.
Preventing Stress Fractures
Preventing stress fractures is essential for athletes who engage in high-impact sports. Some tips to prevent stress fractures include:
- Wearing the right shoes: Athletes should wear shoes that fit well and provide adequate support and cushioning.
- Gradual training: Athletes should gradually increase the intensity and duration of their training to avoid overuse injuries.
- Rest and recovery: Athletes should incorporate rest and recovery into their training regimen to allow their bodies time to heal and recover.
- Proper nutrition: Athletes should maintain a balanced diet that includes adequate amounts of calcium and vitamin D to support bone health.
In conclusion, stress fractures are common injuries among athletes that can cause severe pain and discomfort. Treatment options for stress fractures include rest, ice, compression, elevation and pain relief. Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the injury, and athletes are advised to follow a personalised rehab program for recovery. Contact an experienced osteopath to discuss your case and create a tailored treatment plan for your needs.